Zhepei Weia,b, Jianlin Sud, Yue Wange, Yuan Tiana,b,*, Yi Changa,b,c,*. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2020). Pages 1476–1488.
a. School of Artificial Intelligence, Jilin University
b. Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering, Jilin University
c. International Center of Future Science, Jilin University
d. Shenzhen Zhuiyi Technology Co., Ltd.
e. School of Information and Library Science, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Extracting relational triples from unstructured text is crucial for large-scale knowledge graph construction. However, few existing works excel in solving the overlapping triple problem where multiple relational triples in the same sentence share the same entities. In this work, we introduce a fresh perspective to revisit the relational triple extraction task and propose a novel cascade binary tagging framework (CasRel) derived from a principled problem formulation, as shown in Figure 1. Instead of treating relations as discrete labels as in previous works, our new framework models relations as functions that map subjects to objects in a sentence, which naturally handles the overlapping problem. Experiments show that the CasRel framework already outperforms state-of-the-art methods even when its encoder module uses a randomly initialized BERT encoder, showing the power of the new tagging framework. It enjoys further performance boost when employing a pre-trained BERT encoder, outperforming the strongest baseline by 17.5 and 30.2 absolute gain in F1-score on two public datasets NYT and WebNLG, respectively. In-depth analysis on different scenarios of overlapping triples shows that the method delivers consistent performance gain across all these scenarios.
The source code and data are released online: https://github.com/weizhepei/CasRel
Read more at https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.acl-main.136/
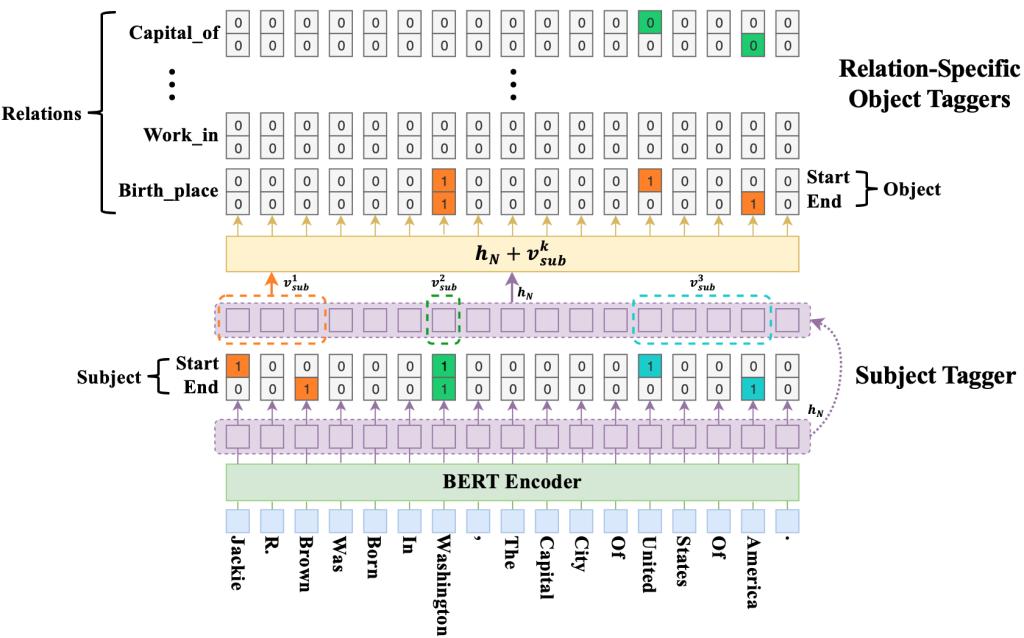
Figure1. An overview of the proposed CASREL framework