Yinghao Liu†, Qiang Zhang†, JunyanLi, Xingxing Wang, Osamu Terasaki, Jun Xu and Jihong Yu
[*]Y. Liu, Dr. Q. Zhang, J. Li, X. Wang, Prof. J. Yu
State Key Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Preparative Chemistry, College of ChemistryJilin UniversityQianjin Street2699, Changchun 130012 (P. R. China)E-mail: jihong@jlu.edu.cn
Prof. J. Yu International Center of Future ScienceJilin UniversityQianjin Street 2699, Changchun 130012 (P. R. China)
J. Li, Prof. O. TerasakiCenter for High-resolution Electron Microscopy (CℏEM), School of Physical Science and TechnologyShanghaiTech University393 Middle Huaxia Road, Pudong, Shanghai 201210 (P.R. China)
K. X. Wang, Prof. J. XuNational Centre for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular PhysicsInnovation Academy for Precision Measurement Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of SciencesWuhan 430071 (P. R. China)
[†] These authors contributed equally to this work
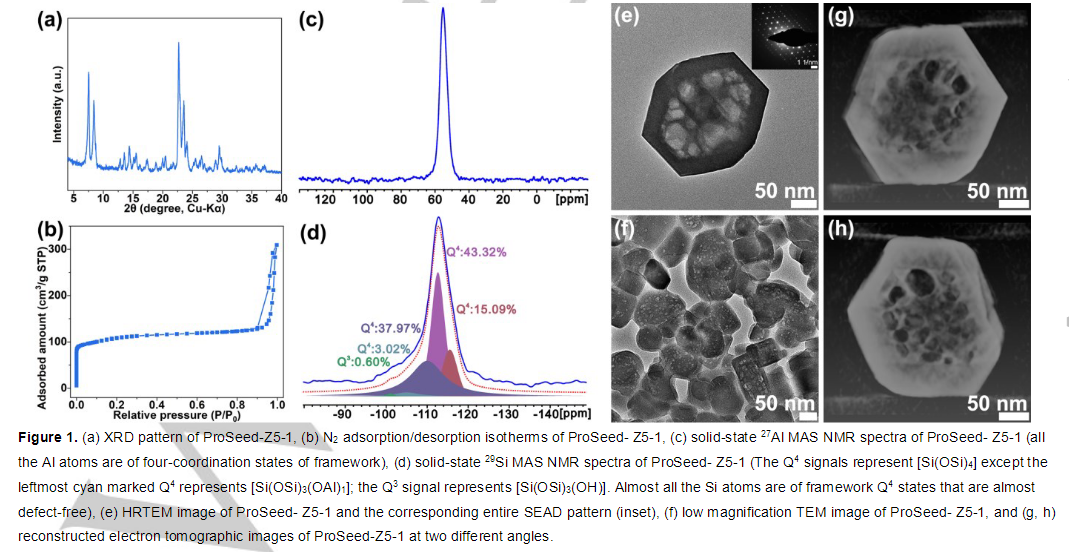
Hierarchical zeolites integrating intrinsic micropores with secondary meso- and/or macropores afford superior catalytic properties for enhanced mass transportation and more accessible active sites. The mesopores generated by using mesoporogens or framework etching are usually irregular with abundant defective sites and low hydrothermal stability. Here, using protozeolite nanoparticles as seeds, we succeeded in the synthesis of single-crystalline hierarchical ZSM-5 zeolites with hexagonal mesopores faceted by complete microporous frameworks. The protozeolites played a key role in the formation of faceted mesopores achieved via intraparticle ripening process. Thanks to the unique texture properties and more accessible acid sites at the open location, the as-prepared zeolites exhibited remarkedly long lifetime (18 h) and high propylene selectivity (52.7 %) with propylene/ethylene ratio of 3.64 in the methanol-to-propylene reaction (WHSV= 12.5 h -1 ) compared to the counterparts.
Related link:
https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202205716